Issues:
Keywords:
This knowledge package focuses on the European Union (EU)’s greenhouse gas targets, specifically, on how they have evolved over time and what progress has been made in achieving them. Detailed information on renewable energy support policies in Europe and energy efficiency targets can be found in the corresponding knowledge packages on this platform. An overview of climate policies implemented in Europe can be found in the Knowledge Package European Climate Policy History and State of Play.
1. From the first IPCC report to the first commitment period
1.1 First IPCC report kicks-off climate discussions in the EU
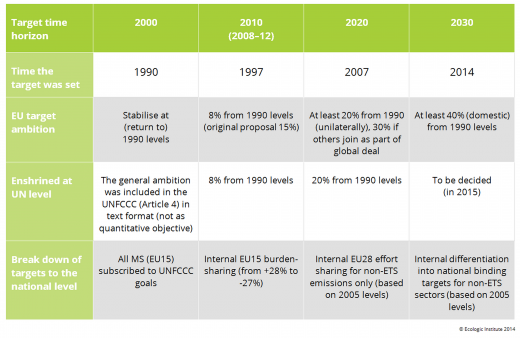
The development of EU climate policy is closely related to the international negotiations organised under the United Nations (UN). It was in 1990, against the backdrop of the first summary report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) and in preparation of the upcoming negotiations on the United Nation Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), that climate change was discussed by the European Council for the first time. In the same year, EU leaders agreed to implement the first European climate target, namely to stabilise greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions of the European Community at 1990 levels by 20001. This target was mainly intended as a signal to the international community about the ambitions of Europe, as EU decision-makers did not determine at that time how the target should be reached or who would do what among its Member States (MS)2.
While the Community tried to promote a joint commitment by the industrialised countries to include this target in the UNFCCC, they were faced with opposition from many countries of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), mainly from the USA3. In 1992, the UNFCCC was adopted and signed with the aim to provide a framework to stabilize “greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere at a level that would prevent dangerous anthropogenic interference with the climate system”4, but without specific targets or measures.
The negotiations on a legal instrument under the UNFCCC started at the first Conference of Parties (COP) in Berlin in 1995. In 1996 the European Community first established its own long-term goal to keep global temperature rise below 2°C compared to pre-industrial levels5. In preparation for the upcoming summit in Kyoto (COP-3) and to foster international commitments to climate change by leading through example, a specific GHG emissions reduction target of 15% in 2010 (compared to 1990 levels) was agreed upon by EU Ministers in early 1997, which the EU would divide internally in a so-called “burden sharing” agreement to introduce specific national targets for all 15 MS (also known as the “EU bubble”). However, a first attempt at compiling a burden sharing agreement by summing up national efforts only came to 9.2%; the further reductions were planned to be realised after an international agreement would come into place6.
1.2 The European Community commits to ambitious reduction targets in Kyoto
At the climate summit in Kyoto in December of 1997 the industrialised countries agreed on a set of quantitative GHG emission targets, with the European Community committing to 8% reductions of a basket of six GHGs during the commitment period 2008-2012 (compared to 1990 levels)7. This was the highest absolute reduction target among the industrialised countries, but still less than the internally agreed reduction goal proposal set out in preparation for Kyoto.
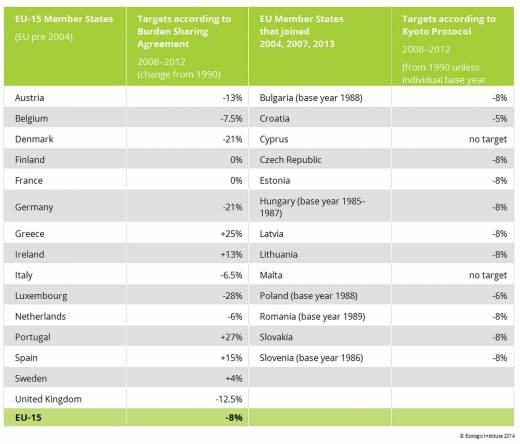
Following the commitments made in Kyoto, an EU internal arrangement was agreed in 1998, which laid down the specific individual targets for the commitment period 2008-2012 for each of the 15 MS to reach the overall reduction of 8%8. In 2002 the Kyoto targets and the burden-sharing agreement were approved9, they became binding Community law in 200410. In addition, a new monitoring mechanism was established to keep track of progress towards the targets11.
The EU expanded by including 10, 2 and 1 Central and Eastern European countries in 2004, 2007 and 2013 respectively. Except for Malta and Cyprus, all of these countries had committed to independent GHG reduction targets under the Kyoto Protocol. Table 1 shows the burden sharing target distribution over the EU-15 countries, as well as the Kyoto targets of the Central and Eastern European (CEE) countries joining the Community in 2004, 2007 and 2013.
2. The "20-20-20 by 2020"-strategy and the second commitment period
In March 2007, as a means of helping to stimulate the UN negotiations on targets for the period after 2012, EU Heads of State agreed on a set of three targets referred to as “20-20-20 by 2020”. It includes
- A reduction of greenhouse gas emissions by at least 20% in comparison to 1990 levels,
- A 20% share of renewable energies in final energy consumption (as well as a 10% target for renewable fuels) and
- 20% of savings on the projected EU final energy consumption in 2020.
Furthermore, the EU included the possibility of a 30% GHG reduction in case there would be a comprehensive and comparable global agreement with similar efforts undertaken by other major developed and developing countries12. Since there was no new international agreement agreed at the 2009 Copenhagen Climate Change Conference for 2020, the EU did not extend the target to 30%.
To implement the targets the EU introduced a set of policies in 2009, known as the “Climate and Energy Package”, which included This package consisted of four main parts:
- a reviewed Directive on emissions trading (ETS Directive)13,
- the Effort-Sharing Decision (ESD)14,
- the Renewable Energy Directive (RED)15, and
- a Directive on carbon capture and storage (CCS Directive)16.
2.1 Overall GHG target consists of EU-wide ETS target and national non-ETS targets
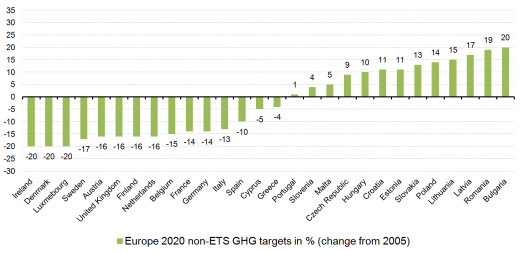
As shown in Figure 1, the amendment of the ETS Directive introduced a single EU-wide emissions cap for emissions from power and industrial installations and thereby effectively abolished national targets in this sector. Around 45% of EU wide emissions are covered by the ETS17. Target fulfilment is to a certain amount linked to Kyoto offset mechanisms (CDM and JI). The Effort Sharing Decision replaces the Burden Sharing Agreement and lays down specific national reduction targets in the non-ETS sectors only. These national targets have been set through a formula based on MS’ relative wealth (measured by Gross Domestic Product per capita). Less wealthy economies can increase emissions, as their higher growth rates are likely to go together with emission increases. Non-ETS sectors include households, buildings, transport, agriculture, services and smaller industrial installations and make up around 55% of EU emissions. The ESD includes the possibility to transfer parts of assigned allocations to subsequent years and to other EU MS. Furthermore it is possible to realise emission reductions by submitting credits from UNFCCC regulated offset projects (under CDM and JI) up to a limit of 3% of non-ETS GHG emissions in 2005 – every year.
2.2 Introduction of EU-wide ETS-sector impedes national emission control
Together the ETS Directive and the ESD regulate the reduction of all GHG emissions of the EU by 20% compared to 1990 levels (i.e. 14% to 2005 levels; 2005 is used as reference year as it is the first year where a split of ETS and non-ETS emissions data was available). The ETS is supposed to contribute 21% reductions in comparison to 2005 levels, the other sectors 10% reductions in comparison to 200518. However, due to the division of the GHG target into an EU-wide target for ETS-sectors and country specific targets for non-ETS sectors it becomes hard for MS to control their overall national emissions, as emissions in the ETS sector are difficult to influence directly. It also makes it impractical to compare the national 2020 targets to those for 2008-2012. The following Figure 2 displays the MS non-ETS targets per MS under the ESD.
The Knowledge Package Progress towards the 2020 climate target in Europe gives a further analysis on the performance of the MS towards their 2020 goals.
3. The post-2020 targets
3.1 EU sets long term emissions reduction target for 2050
In 2009 the EU renewed its commitment to the goal of keeping global warming below 2°C over pre-industrial levels19. EU Heads of State and Government also formally adopted the objective to reduce emissions by 80-95% by 2050 in comparison to 1990 levels. This target was taken from the IPCC’s Fourth Assessment Report, as the share reflecting historic responsibilities, capacities and projected shares of total global emissions of the EU and other Annex 1 countries20. In the Communication entitled “Roadmap to a low carbon economy“, published in May 2011, the European Commission elaborated interim reduction targets for domestic GHG emissions for a cost effective pathway to 80-95% reductions in 2050, of 25% in 2020, 40% in 2030 and 60% in 204021. Since the EU did not adjust its 2020 target following Copenhagen, the 20% is less than the interim target of the roadmap, causing steeper reduction obligations towards 2050 to reach the 80 to 95% reduction goal.
3.2 2030 target framework implements a threefold target set but with lower legal status
In October 2014 the European Council agreed on a new target framework for 2030 that continues the triple target approach of 2020. The greenhouse gas reduction target of at least 40% domestic reductions will be divided into ETS (43% compared to 2005) and non-ETS sector targets (30% compared to 2005), with the latter binding at MS level. However, the legal status of the renewable energy target has been weakened, as the target of 27% will only be binding at EU level22. The energy efficiency target of 27% compared to projections of future energy consumption based will remain an indicative target on the European level. There was a great variety in MS positions regarding the number of targets, the level of target ambition, their legal status (indicative or binding) and whether European action should depend on action outside of Europe (conditionality). This diversity was evident in the responses to a consultation on the topic organised by the European Commission in 201323.
3.3 Setting of targets remains normative and political
While the 2030 GHG target is in line with the interim target of the low carbon economy roadmap of 2011, some stakeholders suggest that steeper reductions are necessary while other stipulate contrarily, that targets should depend on a global agreement. Many target proposals in the debate are underpinned by model estimations with their differing results strongly dependent on the respective underlying assumptions, which make a neutral comparison difficult. The setting of targets remains a rather normative and political decision. From a scientific perspective, targets should follow the precautionary principle and therefore be aiming towards 95% GHG reductions until 2050, which would imply a higher 2030 target than 40%24.
Regarding the renewable energy and energy efficiency targets, environmental non-governmental organisations criticise that these are very close to or even below business as usual scenarios.25 26